From Broadband to Satellite Internet: Understanding Different Types of Internet Services
The internet has become an essential utility in our lives, fueling communication, entertainment, and access to information. But with so many internet service providers (ISPs) and plans available, choosing the right type of internet service can be overwhelming. This article will break down the most common internet connection types, helping you understand their strengths, weaknesses, and which might be the best fit for your needs.
The Backbone: Broadband vs. Dial-Up
Before diving into specific connection types, it’s important to understand the distinction between broadband and dial-up. Dial-up, the traditional method using a phone line, is slow and practically obsolete. Broadband, on the other hand, refers to high-speed internet access that allows for faster data transfer and a more seamless online experience. Most internet connection types discussed below fall under the broadband umbrella.
Wired for Speed: Fiber Optic, Cable, and DSL
Fiber Optic: Often considered the gold standard, fiber optic internet utilizes thin strands of glass to transmit data using light pulses. This translates to blazing-fast speeds, ultra-low latency (the time it takes for data to travel), and exceptional reliability. However, fiber optic installation might not be available in all locations and can be more expensive than other options.
Cable Internet: This popular choice leverages the same coaxial cables used for cable TV to deliver internet access. Cable internet offers good speeds, making it suitable for streaming, online gaming, and everyday internet activities. However, upload speeds can be slower than download speeds, and network performance might be impacted by the number of users sharing the same connection in your area.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line): DSL utilizes existing phone lines to deliver internet access. While not as fast as fiber optic or cable, DSL offers a reliable and affordable option for many users, especially in areas where other options are unavailable. However, DSL speeds can vary depending on your distance from the service provider’s central office.
Wireless: Satellite and Mobile Broadband
Satellite Internet: For those in remote areas where wired options are unavailable, satellite internet provides a lifeline to the online world. It uses satellites in space to transmit data signals, offering wider coverage than wired connections. However, satellite internet suffers from high latency due to the long distances data needs to travel, making it less ideal for real-time applications like online gaming or video conferencing.
Mobile Broadband: With the proliferation of smartphones and mobile data plans, mobile broadband offers internet access on the go. While convenient and readily available, mobile data plans can have data caps and can be expensive, especially for heavy internet users. Additionally, speeds can vary depending on your location and network congestion.
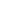
Internet service: IP address
While individual IP address sales are uncommon, some providers offer dedicated IP blocks for businesses seeking more control over their online presence. These packages often come with enhanced security features and may be a better solution for your specific needs.








Leave a Reply